Home / Blogs / The Benefits of MDMA

Welcome to a journey into the world of MDMA, also known as ecstasy or Molly. While often associated with recreational use and party scenes, this powerful substance has gained recognition for its potential therapeutic benefits. In recent years, scientific research has begun to shed light on the positive effects of MDMA in addressing mental health issues such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and anxiety.
MDMA, or 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine, is a synthetic psychoactive substance that alters mood and perception. It belongs to the amphetamine class of drugs and is commonly sold as a tablet or capsule. MDMA is known for its euphoric and empathogenic effects, making it popular in social settings. However, its potential as a therapeutic tool goes far beyond recreational use.
MDMA was first synthesized in 1912 by the German pharmaceutical company Merck. Initially, it was developed as a potential appetite suppressant. However, its psychoactive properties were not recognized until the 1970s when it gained popularity as a recreational drug. In the following decades, MDMA was classified as a Schedule I controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and lack of accepted medical use. Despite this classification, research into its therapeutic potential continued.
MDMA primarily affects the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play crucial roles in regulating mood, emotions, and social behavior. When consumed, MDMA increases the release of these neurotransmitters, leading to heightened feelings of empathy, emotional connection, and euphoria. It also alters sensory perception, enhancing the perception of colors, sounds, and tactile sensations.
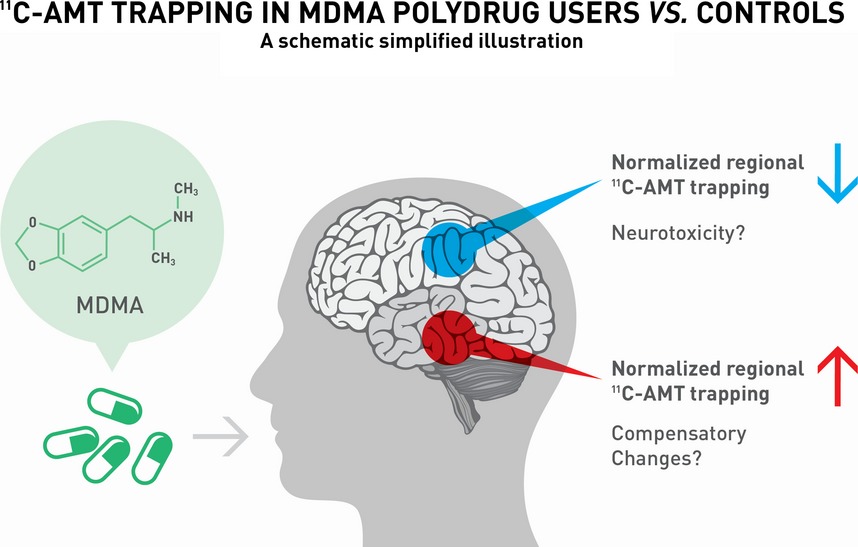
In addition to its acute effects, MDMA can have long-term impacts on the brain. Studies have shown that MDMA use can result in changes to serotonin receptors, which may contribute to altered mood and emotional regulation. However, the extent and permanence of these changes are still being investigated.

While MDMA is currently illegal in most countries, there is growing interest in exploring its potential medical applications. In recent years, clinical trials have been conducted to investigate the use of MDMA in therapeutic settings. These trials have focused on utilizing MDMA-assisted psychotherapy to treat various mental health conditions, particularly PTSD.
MDMA-assisted therapy has shown significant promise in helping individuals with PTSD. In a landmark study published in The Lancet Psychiatry, researchers found that MDMA-assisted psychotherapy resulted in substantial and enduring reductions in symptoms of PTSD. Participants reported increased emotional openness, improved self-esteem, and a stronger sense of connection with others.
One of the key benefits of MDMA in therapy is its ability to enhance empathy and promote emotional processing. By increasing feelings of trust and reducing fear, MDMA creates an optimal environment for individuals to explore and process traumatic experiences. This, in turn, can lead to more effective therapeutic outcomes and long-lasting healing.
MDMA-assisted therapy typically involves a series of sessions conducted under the guidance of trained therapists. These sessions combine the administration of MDMA with traditional psychotherapy techniques, such as talk therapy and cognitive-behavioral interventions. The goal is to help individuals process and integrate traumatic memories in a safe and supportive environment.
Several clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD. For example, a study conducted by the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) showed that 67% of participants who received MDMA-assisted therapy no longer met the criteria for PTSD after just three sessions. These results indicate the potential for MDMA to revolutionize the treatment of PTSD and provide hope for those who have been resistant to other forms of therapy.


While much of the research on MDMA has focused on PTSD, there is growing interest in exploring its potential for other mental health conditions. Preliminary studies suggest that MDMA-assisted therapy may be effective in treating anxiety, depression, and social anxiety disorder. However, further research is needed to fully understand the benefits and limitations of MDMA in these contexts.
Like any psychoactive substance, MDMA carries potential risks and side effects. Acute effects of MDMA can include increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, dehydration, and hyperthermia.
The potential benefits of MDMA in therapy have prompted discussions around its legalization and regulation. Advocacy groups, such as MAPS, have been actively pushing for the rescheduling of MDMA to allow for further research and therapeutic use. In recent years, some countries have taken steps towards decriminalization or medical legalization of MDMA. These developments reflect a growing recognition of the substance’s therapeutic potential and the need for evidence-based approaches to mental health treatment.

The journey into the world of MDMA has revealed its surprising potential as a valuable therapeutic tool. Research has shown that MDMA-assisted therapy can provide profound benefits for individuals struggling with PTSD and other mental health disorders. By enhancing empathy, fostering emotional connection, and promoting emotional processing, MDMA offers new possibilities for healing and therapy.
However, it is crucial to approach MDMA with caution and respect for its potential risks and side effects. Further research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects and determine the optimal conditions for therapeutic use.
As scientific exploration continues, the hope is that MDMA will be recognized for its therapeutic potential and integrated into mainstream mental health treatment options. The benefits of MDMA extend far beyond the party scene, offering a glimmer of hope to those seeking alternative approaches to healing.